Phillips 66 has recently acquired EPIC for $2.2 billion which is a significant move in the NGL market. CEO, Mark Lashier believes that this move will better position Phillips 66 as a downstream energy provider and helps to optimize their NGL value chain.
But what exactly are NGLs and why are they significant?
Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs) are a group of hydrocarbons found in natural gas and crude oil. Most are familiar with “Natural Gas” which is mostly upwards of 95% methane (CH₄). But what are these other NGLs? And how come they are called a natural gas liquids?
NGLs include:
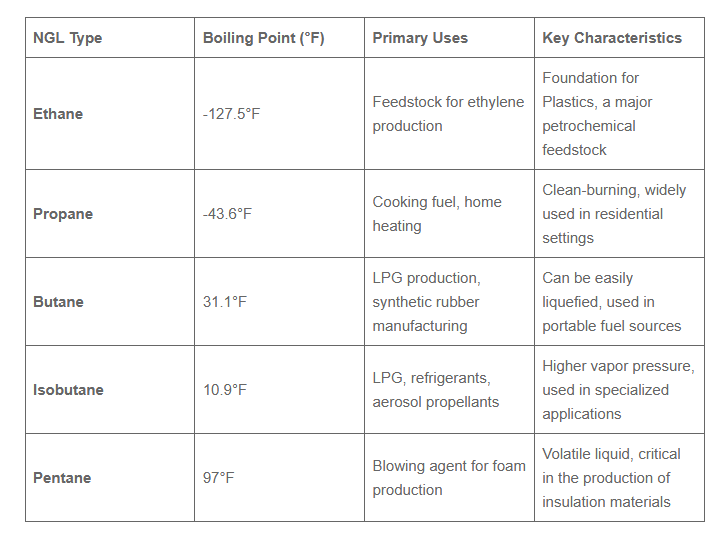
- Ethane (C₂H₆)
- Propane (C₃H₈)
- Butane (C₄H₁₀)
- Isobutane (C₄H₁₀) – same formula as butane but different structure
- Pentane (C₅H₁₂)
NGLs are unique because they can be in liquid form at atmospheric pressure if cooled or compressed, unlike natural gas which remains gaseous under similar conditions.
This is where we get the terms “dry” or “wet” gas. When natural gas is extracted, it is “dry” if it consists of at least 85% methane, but if less than 85% methane and containing as well, liquids like ethane, propane, or butane, it’s “wet”. The higher the methane content, the “drier” the natural gas is.
Regions such as Permian, Bakken, Eagle Ford, Niobrara, and Anadarko are well-known for their “associated gas” (gas from oil wells) which is “wet”, containing NGLs such as ethane, propane, butane, isobutane, etc.
So why are these NGLs important?
1. NGLs are incredibly versatile in their usage within a variety of industries. They are essential in petrochemical plants as they serve as building blocks for products like plastics, synthetic rubber, and other materials.
2. NGLs enhance the profitability of natural gas production by providing additional revenue streams. They are valuable products that can be sold separately.
3. NGLs like propane are widely used for heating, cooking, and as fuel for vehicles. They are crucial in areas without access to natural gas pipelines, making them strategic resources globally.
What about usage of NGLs within developing countries?
In the developing world, NGLs can play a significant role in improving energy access and economic development. The United Nations and its affiliated organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), have highlighted the significant health and environmental benefits of replacing traditional wood fuels with cleaner alternatives like Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
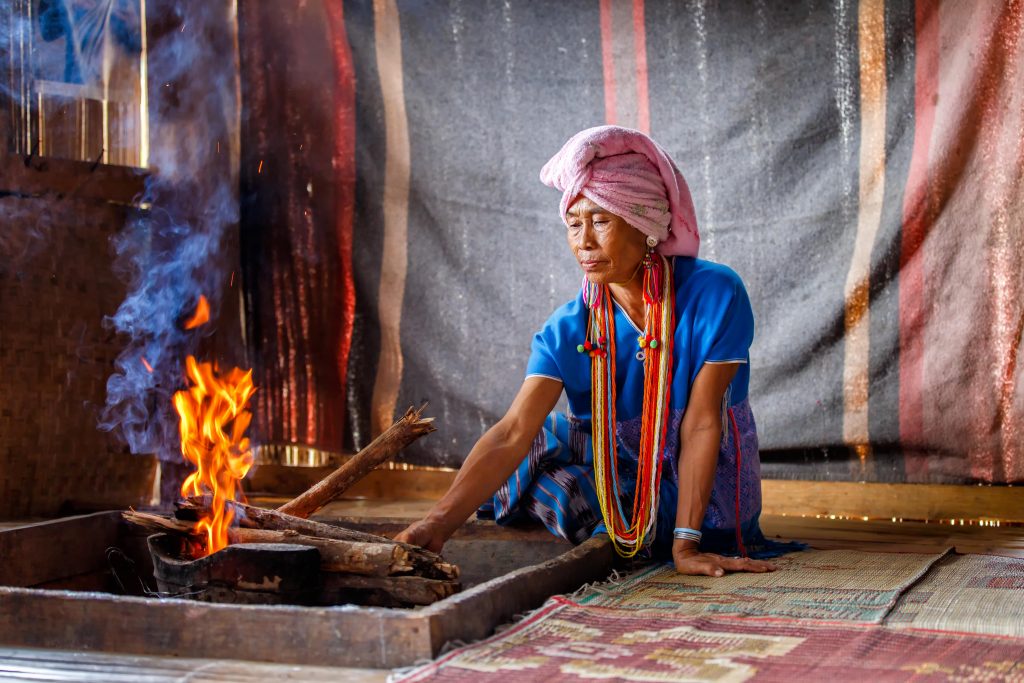

Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) primarily consists of NGLs such as propane (C₃H₈) and butane (C₄H₁₀) and is produced during the processing of natural gas and the refining of crude oil. It is stored in pressurized containers to maintain its liquid form.
LPG is a cleaner alternative to traditional biomass fuels used for cooking and heating, reducing health risks associated with indoor air pollution. Additionally, the development of NGL infrastructure can create jobs and stimulate local economies.
The State of the NGL Market:
The US NGL market is substantial, driven by significant natural gas production, particularly from shale formations. The market is expected to continue growing, with increasing investments in infrastructure and production capabilities.
The global NGL market was valued at approximately $20.05 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $28.68 billion by 2029, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.99% fueled by rising demand from the petrochemical industry and the transition to cleaner fuels.
This acquisition bolsters Phillips 66’s position in the Permian Basin, a major hub for NGL production; it includes long-haul NGL pipelines, fractionation facilities, and distribution systems, enhancing Phillips 66’s ability to transport and process NGLs to better serve producers and meet growing demand for NGLs, both domestically and internationally.
How would one create a robust model of the NGL market to simulate future possibilities?
1. Data Collection on NGL production, transportation, and consumption.
2. Input proprietary assumptions into the simulator’s database to create a reference case.
3. Develop various scenarios to explore different market conditions and their impacts.
4. Use the simulator to run market simulations and generate forecasts.
5. Analyze the simulation results to inform investment decisions, policy development, and strategic planning.
RBAC has created the most advanced tools for modeling the Natural gas market, including Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs) through their NGL-NA® Market Simulator. This simulator is designed to provide comprehensive market analysis and forecasting for the North American NGL market. Through integration of extensive data on NGL production, transportation, and consumption, and users can simulate the market under various conditions.
Would you like to know more?
Contact RBAC here for further information.


